
Acetic acid has a lot of uses, but there are some hazards linked to it as well.
This post helps you to learn about these hazards and the safety measures to apply when handling acetic acid in addition to other valuable information about the chemical.
Please, read on:
Acetic acid may not sound like a common name but it is useful in a lot of ways across different industries. It is a colorless, pungent smelling liquid with a characteristic sour taste.
Acetic acid goes by other names like ethanoic acid (in scientific circles) and glacial acetic acid when undiluted.
Acetic acid is the main component in vinegar, the other being water.
What is Acetic Acid?
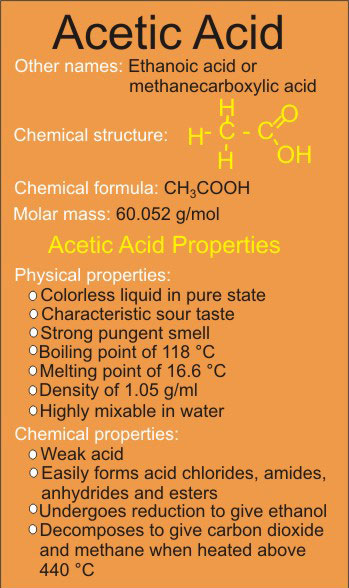
Acetic acid, is a colorless liquid that is identified as ethanoic acid or methanecarboxylic acid, it has a distinct and strong pungent smell, as well as sour taste.
The chemical formula for acetic acid is represented as CH3COOH: There are two carbon (C) atoms, four hydrogen (H) atoms and two oxygen (O) atoms.
Acetic acid is an organic compound since there is a carbon in its chemical formula,
Here are different ways to represent the chemical formula of acetic acid:
- C2H4O2
- CH3COOH
- CH3CO2H
Acetic acid is regarded as a weak acid since it dissociate in a solution, but an acid nonetheless; when concentrated, it can be corrosive if it touches the skin.
Acetic Acid: Hazard, Safety and Disposal
Here are typical hazard, safety and disposal methods for acetic acid:
Common Acetic Acid Hazards
Acetic acid is highly corrosive liquid that can be lethal if not used in a safe and proper manner.
The skin and eyes can be damaged from contact and it is dangerous to the internal organs if inhaled or ingested. It is advisable to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling this chemical especially when it is not diluted.
Acetic acid is hazardous when there is eye or skin contact and if inhaled. The symptoms range from irritation of the eyes, nose, skin, and throat.
Others include eye and skin burns; skin sensitization; black skin, conjunctivitis, hyperkeratosis; lacrimation (discharge of tears); pharyngeal edema, chronic bronchitis; dental erosion, etc.
Acetic Acid Safety Handling Procedures
When handling acetic acid, you want to follow recommended caution:
- Do not add water to the chemical
- Ensure the chemical is kept far away from sources of heat, flame and sparks
- When in an area not well-ventilated, ensure you wear appropriate respiratory equipment like synthetic apron, splash goggles, gloves, vapor respirator (if needed)
- It is advisable to have eye-wash stations nearby when handling acetic acid.
In emergency cases where there is a large spill either at home or the workplace, wear a self-contained breathing apparatus as well as full protective suit for additional safety.
NB: Do not attempt to clean up the acetic acid if you do not have this equipment readily at hand.
Acetic Acid Safety Storage Procedures
Acetic acid should be stored in a tightly sealed container, in a cool, well-ventilated area. It should be kept far away from heat sources, flames, and sparks – from all sources of ignition.
It should be kept away from discordant materials like metals, acids, alkali, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents.
Safety is the top priority when handling chemicals like acetic acid. Care must be taken when using this corrosive liquid both at the workplace and in the home.
Acetic Acid Safety Disposal Procedures
Disposal of acetic acid must follow federal, state, and local regulations and use suitable personal protective equipment.
You should decontaminate equipment and bench tops with soap and water.
All contaminated disposables and chemical tagged as hazardous must be disposed following proper guidelines.
Label Waste
Waste should be labeled properly as soon as the first drop of waste is added to the container using waste tags in line with the online tag program, go here to learn more http://otp.ucop.edu/
Store Waste
Hazardous waste should be stored in a tight container, place in another casement and in a specified location.
- Dry waste should be double-bagged using transparent bags
Dispose of Waste
- Generated chemical waste should be disposed within 90 days
- You can call EH&S at 228-7864 for any questions
- Look up http://ehs.ucla.edu/Pub/ExtremelyHazardousWaste.pdf for any other information.
How to Handle Exposures to Acetic Acid
Acetic acid can be dangerous in any form of exposure, apply first aid and then seek medical attention.
Skin Contact – flush with water for at least 15 minutes and remove any contaminated clothing. Get medical attention immediately
Eye Contact – if wearing contact lenses remove immediately. Irrigate with plenty water for no less than 15 minutes. Get medical help as soon as possible.
Ingestion – Do not induce vomiting, if acetic acid is ingested. Do not administer any mouth-to-mouth resuscitation, if victim is unconscious. Undo any tight clothing. Get medical attention quickly.
Inhalation – seek fresh air and medical attention immediately, if inhaled. Administer oxygen if breathing is difficult. Give artificial respiration if breathing is absent.
Acetic Acid Properties
Acetic acid possesses some properties that have implication on its use and preparation. Here are the properties it usually exhibits:
Physical properties
Pure acetic acid is a colorless liquid with a characteristic sour taste and a strong pungent smell.
It has a boiling point of 118 °C, melting point of 16.6 °C, and a density of 1.05 g/ml.
Acetic acid has molar mass of 60.052 g/mol and is highly mixable in water.
Chemical properties
Acetic acid is classified as a weak acid. It is one of the carboxylic acids that easily form acid chlorides, amides, anhydrides and esters.
It undergoes reduction to give ethanol (reduction is a chemical process that result in removal of oxygen or addition of hydrogen).
Acetic acid decomposes to give carbon dioxide and methane when heated above 440 °C.
CH3COOH → CH4 + CO2
Acetic Acid Preparation
Acetic acid can be produced by bacterial fermentation (in large quantity) and chemical synthesis. When alcoholic food sources (such as rice, grain, malt, wine, etc.) go through bacterial fermentation it produces acetic acid by the oxidation of ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH).
C2H5OH + O2 → CH3COOH + H2O
Using chemical method, the reaction of methanol (CH3OH) with carbon monoxide will yield acetic acid with rhodium-iodine serving as a catalyst.
CH3OH + CO + Rh/I2 → CH3COOH
Acetic Acid Uses
Acetic acid is used as vinegar in the food industry, as well as a solvent for resins and paints. It is also used as an acidity regulator.
Acetic acid is one industrial reagent used for producing different chemicals such as metal acetates, polyvinyl acetate, cellulose acetate, etc.
Conclusion
Acetic acid has several uses across many industries. It is a corrosive liquid that must be handled with care.
This article provides useful information regarding hazards, storage, and disposal of acetic acid.
