
If you have a need to handle acetonitrile, there are possible hazards involved with the chemical that you need to be aware of to keep yourself and others in the environment safe.
This post provides exhaustive information you can use to learn about acetonitrile hazards, how to safely store and dispose of the chemical, etc.
Please, continue reading:
What is Acetonitrile
Acetonitrileis a chemical compound that has the formula CH3CN. This colorless substance is the simplest organic nitrile. Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion (CN–) is not classed as organic.
Acetonitrile is manufactured mainly as a by-product of acrylonitrile and is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the cleansing of butadiene.
Acetonitrile Structure
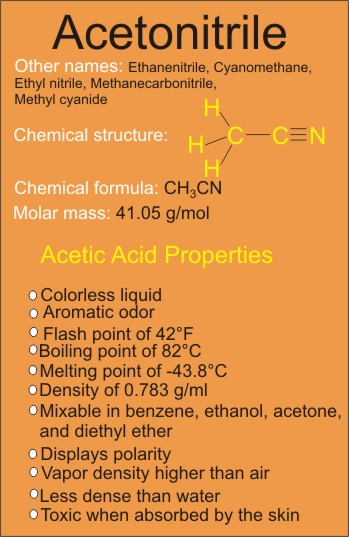
The acetonitrile structure as seen in the above diagram consists of the organic methyl group (simplest hydrocarbon group) bonding to the triple bond cyanide or nitrile group (C≡N) with a bond angle of 180 degrees between the two groups.
The bonding between the methyl group and the nitrile group makes acetonitrile the simplest organic nitrile available.
Common Acetonitrile Hazards
Here are common hazards associated with acetonitrile:
Inhalation
The outcome of excessive exposures to acetonitrile is often delayed because of the slow formation of cyanide anions in the body.
These cyanide anions stop the body from having oxygen and can cause internal asphyxiation. Initial symptoms may include nose and throat irritation, flushing of the face, and chest tightness.
High concentrations could lead to headache, vomiting, and airway problems; feebleness, blood changes, and thyroid changes; unbalanced heartbeat, gut pain, and convulsions; shock, blackout, and passing away.
Ingestion
Gastric irritation may occur if swallowed. Other signs that may be shown are similar to those displayed from inhalation exposure.
Skin contact
If acetonitrile touches the skin, it may lead to irritation since it can be absorbed through skin with health effects to similar to those from inhalation.
Eye contact
Splashes often lead to eye irritation, discomfort, redness, and pain.
Chronic exposure
Exposures to acetonitrile for a long period of time may affect kidneys, liver, and the central nervous system.
Acetonitrile Safety Handling Procedures
When handling acetonitrile, you need to be extremely cautious. Make sure you remove polluted clothing and wash before reuse.
Use only in a well-ventilated area or an open space filled with fresh air. Never inhale dust, vapor, mist, or gas.
Never allow it to contact the eyes or touch the skin, or spill on clothing. Always empty containers having a remnant of the chemical (liquid and/or vapor).
Preserve container firmly closed. Avoid contact with flame, heat, or sparks. Never swallow or breathe in, and never dispose or expose empty containers to open flame, heat, or sparks.
Acetonitrile Safety Storage Procedures
Acetonitrile should be stored in a cool and dry location where there is ventilation, far away from any environment where fire hazard may be critical.
Detached or outside storage is ideal. Isolate from incompatibles.
Containers should be grounded and bonded for transfer in order to avoid static sparks. Smoking should not be allowed around the storage environment.
Utilize non-sparking type tools and equipment, as well as explosion resistant ventilation. Containers of this material may be dangerous when empty since they have remnants of the product in them (vapors or liquid).
Detect and abide with all warnings and safety measures listed for the product. Never endeavor to clean empty containers since remnant is hard to remove.
Acetonitrile Safety Disposal Procedures
Acetonitrile should to be disposed properly after use; otherwise, you may end up experiencing hazards.
Whenever you make use of acetonitrile, carefully follow this procedure in order to dispose them properly.
- Ensure the glass container or metal is sealed to store up acetonitrile remnant before disposing it. Avoid using plastic.
- Store container in a dry and secluded environment.
- When taking container for disposal, ensure the integrity of the container to prevent leakage.
How to Handle Exposures to Acetonitrile
If you inhale acetonitrile, move to a place with enough ventilation. If you find it difficult to breathe, call for medical help instantly.
If acetonitrile touches your skin, wash with soap and lot of water for 15 to 20 minutes. Pull off any clothes or shoes that have acetonitrile on them.
If acetonitrile enters into your eyes, flush with lots of water for 15 to 20 minutes. Call for medical attention immediately.
Acetonitrile Properties (Chemical and Physical)
One of the most significant properties of acetonitrile is its polarity. More specifically, it is categorised as a polar compound. What does this mean exactly?
As shown in the diagram above, the nitrogen atom bonding to a carbon atom in the nitrile group is more electronegative than the carbon and so will pull the shared electrons between the two of them more closely to itself than to the carbon atom.
The result of the pull of shared electrons more to the nitrogen atom will cause partial negative charge on the nitrogen and partial positive charge on the carbon, which explains the why acetonitrile molecule is polar.
Another significant property is its boiling point, which is estimated to be about 82 degree Celsius. It is really a rather high boiling point for such a little molecule, the rate of the boiling point can really be attributed to the polarity.
Generally, the more polar a compound is, the higher the boiling point will become.
Other properties of acetonitrile include melting point of -43.8°C; density of 0.783 g/cm3; and flash point of 42°F.
Acetonitrile is a colorless liquid which is less dense than water, and has an aromatic odor. It has vapor density higher than air and is toxic when absorbed by the skin.
Acetonitrile is quit miscible with benzene, ethanol, acetone, and diethyl ether.
Acetonitrile Preparation
Acetonitrile is the chief by-product during the making of acrylonitrile via the ammoxidation of propene and/or propane.
The discriminating change of acetonitrile to acrylonitrile is a promising way for the utilization of the previous nitrile since the market’s demand is significantly lower than the availability.
A possible way for this reaction to occur is by passing it over basic catalysts through the addition of a carbon atom at the α-position of the acetonitrile.
Many investigators in the past have utilized molecules such as methanol, methane, and formaldehyde as methylation agents for this reaction.
Acetonitrile Uses
Acetonitrile is used to manufacture pharmaceuticals, rubber, and perfume products; pesticides, acrylic nail removers, and batteries.
It is also utilized in removing fatty acids from animal and vegetable oils.
Conclusion
Acetonitrile is a valuable substance used in producing a lot of useful items. Caution must be applied when handling this chemical in order to prevent hazards or accidents.
This article provides useful information about acetonitrile with a guide to help you handle hazards related to it.
